Spring Authentication
Authentication is the process of recognizing a user’s identity. It is the mechanism of associating an incoming request with a set of identifying credentials. The credentials provided are compared to those on a file in a database of the authorized user’s information on a local operating system or within an authentication server
Difference between Authentication and Authorization
Authentication: mainly Authentication for asking a user, Who are you?
Authorization: to know what access control a user has, What are you allowed to do/see?
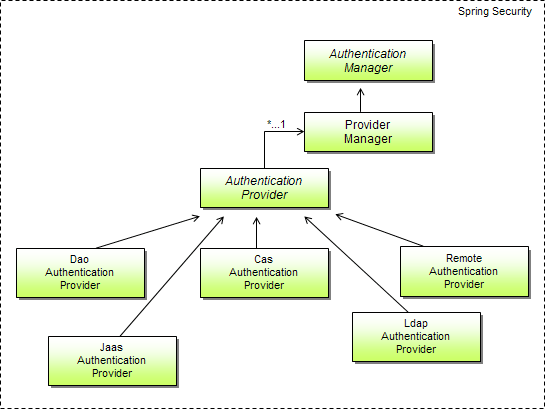
as shown in the image above, the main strategy in Spring Authentication is AuthenticationManger intergace which has only one method:
public interface AuthenticationManager {
Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication)
throws AuthenticationException;
}
According to Spring-Authentication-Documentation an AuthenticationManager can do one of 3 things in its authenticate() method:
-
Return an Authentication (normally with authenticated=true) if it can verify that the input represents a valid principle.
-
Throw an AuthenticationException if it believes that the input represents an invalid principle.
-
Return null if it cannot decide.
The most commonly used implementation of AuthenticationManager is ProviderManager, which delegates to a chain of AuthenticationProvider instances. An AuthenticationProvider is a bit like an AuthenticationManager, but it has an extra method to allow the caller to query whether it supports a given Authentication type:
public interface AuthenticationProvider {
Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication)
throws AuthenticationException;
boolean supports(Class<?> authentication);
}