Linked List
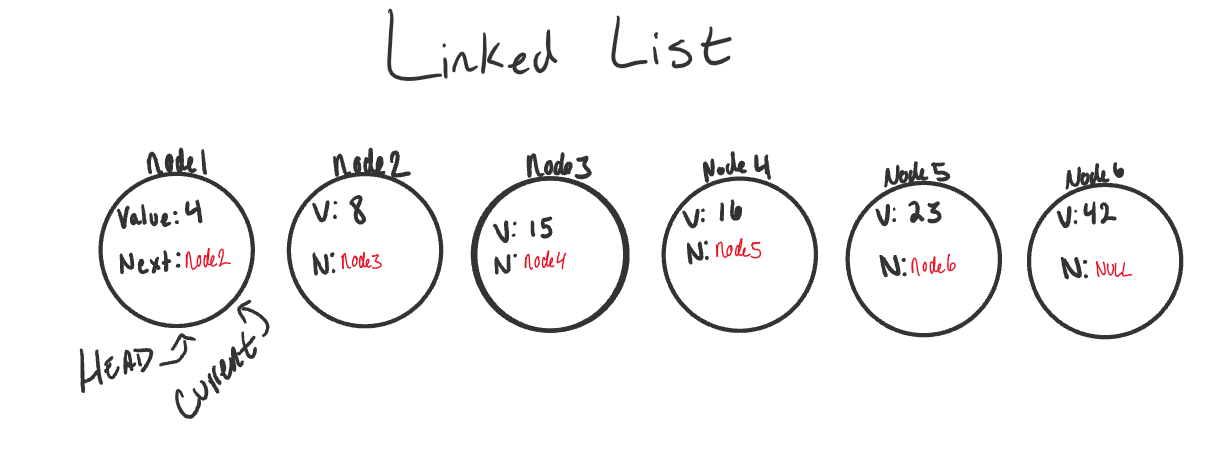
A Linked List is a sequence of Nodes that are connected/linked to each other. The most defining feature of a Linked List is that each Node references the next Node in the link.
Example of linked list class in java
public class LinkedList {
Node head;
public LinkedList(){
head = null;
}
static class Node{
int value;
Node next;
public Node(int v){
value = v;
next = null;
}
}
public void insert(int n){
Node node = new Node(n);
if (head == null) {
head = node;
}else{
node.next = head;
head = node;
}
}
public boolean includes(int n){
boolean found = false;
Node current = head;
while(current!= null){
if(current.value == n){
System.out.println(current.value);
found = true;
break;
}
current = current.next;
}
return found;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
String result = "";
Node current = head;
while(current != null){
result+="{" + current.value + "} -> ";
current = current.next;
}
return result + "NULL";
}
}
and anthor class the inherits the LinkedList.java class is FullLinkedList.java link
because of java arrays have fixed length and once the array created, it does not allow to add any new element.
in short linked list is a dynamic array to add elements and the limit of linked list is the memory size.
there are three types of linked list
- singly linked list where you can loop over the elements in one way
- double linked list where you can loop forward and backward the linked list
- circular linkedlist where the last element points to the first element in the list.